Our Services
Speech Language Therapy
Speak Easy Rehabilitation offers adult and pediatric patients in all therapeutic areas. We offer speech language therapy, occupational therapy, physical therapy, and developmental all in one practice.
Pediatric Speech Language Therapy
Adult & Geriatric Speech Language Therapy
Articulation Disorders
A speech disorder involving difficulties in articulating specific types of sounds. Articulation disorders often involve substitution of one sound for another, slurring of speech, or indistinct speech.
Auditory Processing Disorders
Auditory processing disorder (APD) is a hearing problem that affects about 5% of school-aged children. Kids with this condition, also known as central auditory processing disorder (CAPD), can’t process what they hear in the same way other kids do. This is because their ears and brain don’t fully coordinate.
Augmentative/Alternative Communication (AAC)
Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurological and developmental disorder that begins early in childhood and lasts throughout a person’s life. It affects how a person acts and interacts with others, communicates, and learns. It includes what used to be known as Asperger syndrome and pervasive developmental disorders.
Genetic Disorders and Syndromes
A syndrome is a disease or disorder that has more than one identifying feature or symptom. Each particular genetic syndrome will have many typical features, depending on which aspects of development are affected by the abnormal genes or chromosomes.
A child might be born with obvious body deformities, abnormal organ function (for example: heart, brain, gut, or kidney), or neurological problems (for example, when a baby’s body is floppy or the baby is unable to nurse or bottle feed). However, many of the genetic syndromes start to take effect only once the baby has been born and is starting to feed and grow. These babies may look and act entirely normal at birth, but then develop problems later on in life.
Receptive/Expressive Language Disorders
Mixed receptive–expressive language disorder (DSM-IV 315.32) is a communication disorder in which both the receptive and expressive areas of communication may be affected in any degree, from mild to severe. Children with this disorder have difficulty understanding words and sentences.
Phonological Processing Disorders
A phonological process disorder is a form of speech disorder in which there is difficulty organizing the patterns of sounds in the brain which results in an inability to correctly form the sounds of words.
Pragmatics and Social Skills
Pragmatic language refers to the social language skills that we use in our daily interactions with others. This includes what we say, how we say it, our non-verbal communication (eye contact, facial expressions, body language etc.) and how appropriate our interactions are in a given situation.
Stuttering/Cluttering Disorders
Like stuttering, cluttering is a fluency disorder, but the two disorders are not the same. Cluttering involves excessive breaks in the normal flow of speech that seem to result from disorganized speech planning, talking too fast or in spurts, or simply being unsure of what one wants to say. By contrast, the person who stutters typically knows exactly what he or she wants to say but is temporarily unable to say it. To make matters even more confusing, since cluttering is not well known, many who clutter are described by themselves or others as “stuttering.” Also, and equally confusing, cluttering often occurs along with stuttering.
Swallowing/Feeding Disorders
Swallowing disorders, or dysphagia, are a type of feeding disorder in which the child has physical difficulty swallowing. Swallowing is more complex than you might think: your tongue, mouth and throat muscles make more than a dozen different movements to swallow.
Cognitive-Linguistic Disorders
A person with a cognitive-communication disorder may have difficulty paying attention to a conversation, staying on topic, remembering information, responding accurately, understanding jokes or metaphors, or following directions.
Cognitive-communication disorders vary in severity. Someone with a mild deficit may simply have difficulty concentrating in a loud environment, whereas a person with a more severe impairment may be unable to communicate at all.
Dysarthria & Apraxia (speech-articulation disorders)
Dysarthria is a motor speech disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor-speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes.
Apraxia of speech (AOS)—also known as acquired apraxia of speech, verbal apraxia is a speech sound disorder. Someone with AOS has trouble saying what he or she wants to say correctly and consistently. AOS is a neurological disorder that affects the brain pathways involved in planning the sequence of movements involved in producing speech. The brain knows what it wants to say, but cannot properly plan and sequence the required speech sound movements.
Augmentative/Alternative Communication (AAC)
Language Deficits
Language deficits are problems with age-appropriate reading, spelling, and writing. The language disorder that comes most readily to mind is dyslexia, which is a difficulty in learning to read. But many students who have problems with reading have spoken language problems as well, and for that reason, language deficits or language disorders are the more inclusive ways to speak about these issues.
Swallowing Difficulties
Difficulty swallowing is also called dysphagia. It is usually a sign of a problem with your throat or esophagus —the muscular tube that moves food and liquids from the back of your mouth to your stomach. Although dysphagia can happen to anyone, it is most common in older adults, babies, and people who have problems of the brain or nervous system.
Voice Problems
A voice disorder occurs when the pitch, loudness, or quality of the voice distracts from what the speaker is saying. It is also a problem if the speaker experiences pain or fatigue when speaking or singing. There is also a laryngeally based respiratory disorder called vocal cord dysfunction (or paradoxical vocal fold motion) that does not always include changes to the voice but often has symptoms of chronic cough or throat clearing, odor sensitivities, and shortness of breath.
Aphasia
Aphasia is the loss of ability to understand or express speech, caused by brain damage.
Brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) is defined as a blow to the head or a penetrating head injury that disrupts the normal function of the brain. TBI can result when the head suddenly and violently hits an object or when an object pierces the skull and enters brain tissue.
Stroke
Stroke is a disease that affects the arteries leading to and within the brain. It is the No. 5 cause of death and a leading cause of disability in the United States. A stroke occurs when a blood vessel that carries oxygen and nutrients to the brain is either blocked by a clot or bursts (or ruptures).
Dementia
Dementia is a collective term used to describe various symptoms of cognitive decline, such as forgetfulness. It is a symptom of several underlying diseases and brain disorders. Dementia is not a single disease in itself, but a general term to describe symptoms of impairment in memory, communication, and thinking.
Other Neurological Conditions
Speak Easy Speech Rehabilitation can help with almost any condition or combination of issues. Call us today to arrange for a consultation appointment.
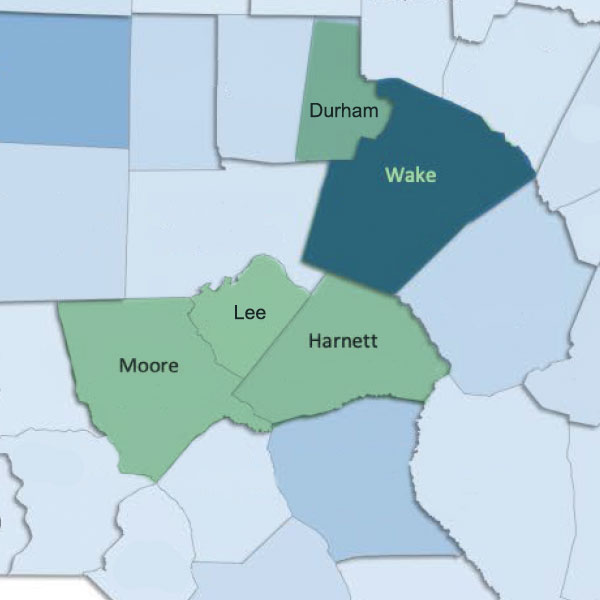
Our Service Areas
We provide therapy services to the following counties.
Wake County
Including Holly Springs, Cary and Apex
Durham County
Harnett County
Lee County
“Angie is very kind and warm to my son who, at times, has a hard time with people. We have seen improvement since starting speech and I am excited to see his future improvements. I am very happy with Angie.“

AK
Parent of Speak Easy Rehabilitation child
Your Rehabilitation, Your Habilitation, Your Recovery is Our Mission.
CALL, EMAIL OR MAKE YOUR APPOINTMENT ONLINE
919.346.3350
336.447.6113
Mailing Address
PO Box 2023
Fuquay Varina, NC 27526